[Network] 1. 네트워크 기본 : Network 구성요소, TCP vs UDP, 서킷 스위칭 vs 패킷 스위칭, 패킷 딜레이

Network Structure : 네트워크 구성요소
1. network edge :
- applications and hosts
2. network core :
- routers
3. access networks, physical media :
- communication links 라우터들을 연결시켜주는 링크
1. network edge :
1) end systems (hosts) : run application programs
eg) Web, email
2) client/server model : client host requests, receives service from always-on swerver
eg) web browser/server; email client/server
3) peer-peer model : minimal use of dedicated servers
eg) Skype, BitTorrent
데이터 통신방식
1. connection-oriented service
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- reliable : 신뢰할 수 있음
- flow control : 수신자 능력 고려하여 받을 수 있는 만큼 전송
- congestion control : 네트워크 막힘현상시 속도 낮춰서 전송
사용: HTTP, FTP, Telnet, SMTP(email)
2. connectionless service
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- connectionless
- unreliable data transfer
- no flow control
- no congestion control
사용: Streaming media, DNS
2. network core :
라우터간의 연결들의 집합
네트워크를 통한 데이터 전송방식
1. circuit switching :
출발지에서 목적지까지 가는 길을 미리 설정

bandwidth 가 1Mpbs이고 1명의 유저당 active 상태에서 100kb/s 사용시 최대 10명의 유저만 사용가능
2. packet-switching :
패킷 순서가 정해져있지 않으며 패킷을 요청시 공유한다. (statistical multiplexing )
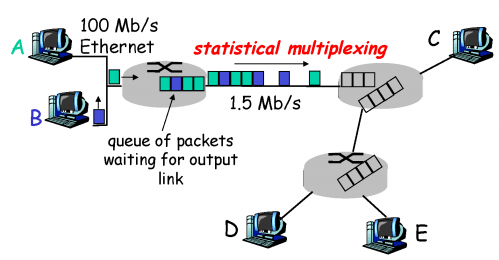
패킷 딜레이
1) nodal processing
check bit errors : 패키지 검사
2) queueing : 큐 순서 기다리기
※ queue 가 초과하는 경우 packet 이 유실된다. (대부분의 packet 유실은 queue 초과로 일어난다)
3) Transmission delay
R = link bandwidth(bps)
L = packet length (bits)
L/R : time to send bits into lnk
: 큐 순서 도달 후, 시작 bit 부터 끝 bit 까지 link 를 통해 bit가 나가는데 총 걸리는 시간
4) Propagation delay :
d = length of physical link
s = propagation speed in medium (광속)
d/s = propagation delay
패킷 딜레이를 줄이려면?
1) processing delay : 라우터 성능 업그레이드
2) queueing delay : 사용자 수에 의해 결정되므로 제어 불가
3) transmission delay : 케이블 업그레이드
4) propagation delay : 광속이므로 제어 불가
※ 한양대학교 이석복 교수님의 컴퓨터네트워크 강의 내용 정리