[ Route53 ]
- Route53 is a Managed DNS (Domain Name System)
- DNS is a collection of rules and records which helps clients understand how to reach a server through its domain name
* You pay 0.5$ per month per hosted zone
- In AWS, the most common records are :
1) A : host name to IPv4
2) AAAA : hostname to IPv6
3) CNAME : hostname to hostname
4) Alias : hostname to AWS resource
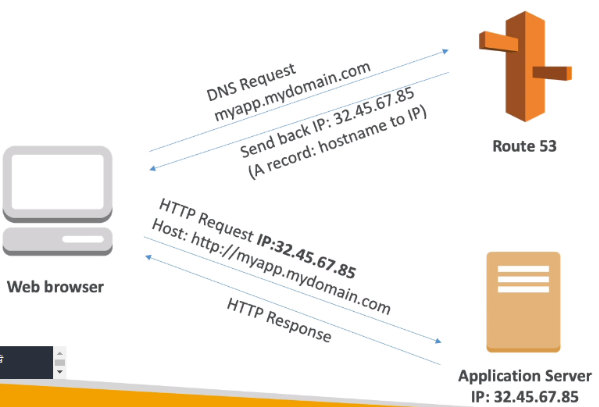
- Route 53 can use :
public domain names you own (or buy)
private domain names that can be resolved by your instances in your VPCs.
- Route 53 has advanced features such as :
Load balancing (through DNS - also called client load balancing)
Health checks (although limited..)
Routing policy : simple, failover, geolocation, latency, weighted, multi value
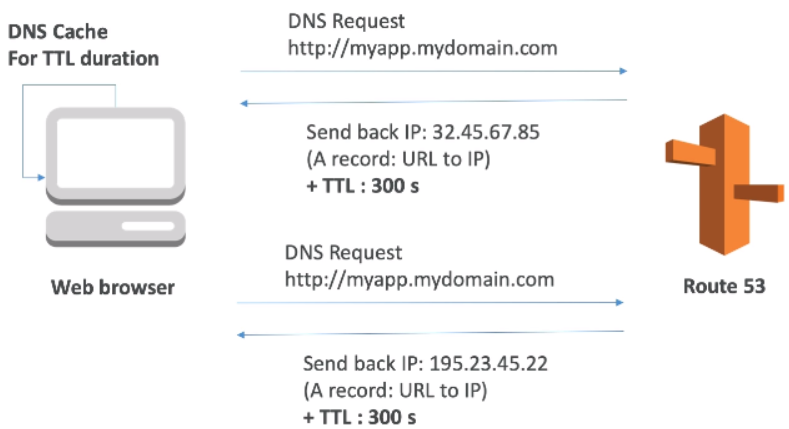
[ DNS Records TTL (Time to Live) ]
Web browser cache 가 살아있는 시간.
Web browser 는 Route 53 에 DNS 요청을 하고 도메인에 해당하는 IP와 함께 TTL을 받아 TTL 시간동안 DNS 를 캐싱한다. TTL이 다 지날 경우 다시 DNS 요청을 하여 IP를 다시 캐싱한다.
TTL 시간이 길 수록 DNS 트래픽은 줄어들고 웹브라우저가 옛날 아이피로 요청할 가능성이 높아진다. (DNS 의 A record설정을 수정할 경우)
TTL 값은 필수 DNS record
- High TTL (eg. 24 hour)
Less traffic on DNS, Possibly outdated records
- Low TTL (eg. 60 seconds)
More traffic on DNS, Records are outdated for less time, Easy to change records
* TTL is mandatory for each DNS record
[ CNAME vs Alias ]
CNAME 은 도메인(호스트) 호출시 다른 호스트명으로 리다이렉트, 유료, 도메인은 사용 불가, 유료
Alias 는 도메인(호스트) 호출시 AWS 리소스로 리다이렉트, root 도메인도 사용 가능, 무료
CNAME :
- Points a hostname to any other hostname (app.mydomain.com > blabla.anything.com)
- only for Non Root domain (eg. something.mydomain.com)
- not free
Alias :
- Points a hostname to an AWS Resource (app.mydomain.com > blabla.amazonaws.com)
- Works for Root domain and non root domain (eg. mydomain.com)
- Free of charge
- Native health check
[ Simple Routing Policy ]
1개의 CNAME/Alias 에 1개의 A record 지정한 1:1 관계. health check 사용 불가
1개의 CNAME/Alias 에 2개 이상의 A record 가 지정되있을 경우 client 가 랜덤으로 IP 선택
- Use when you need to redirect to a single resource
- You can't attach health checks to simple routing policy
* If multiple values are returned, a random one is chosen by the client
(=client side load balancing)
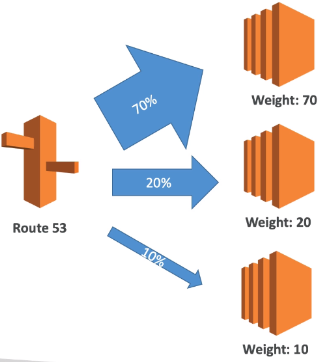
[ Weighted Routing Policy ]
A record 마다 가중치를 다르게 주어 트래픽을 분산하는 정책
- Control the % of the requests that go to specific endpoint
- Helpful to test 1% of traffic on new app version for example
- Helpful to split traffic between two regions
- Can be associated with Health Checks
[ Latency Routing Policy ]
최저응답시간을 갖는 A record 로 리다이렉트 시키는 정책
(eg. 한국/미국/영국 region 의 인스턴스를 latency routing policy 를 적용하여 하나의 CNAME 의 A record 로 지정한 후 서울에서 DNS 요청시 한국 A record 의 인스턴스가 응답함)
- Redirect to the server that has the least latency close to us
- Super helpful when latency of users is a priority
- Latency is evaluated in terms of user(사용자 측면에서) to designated(지정된) AWS Region (유저마다 최저응답시간을 갖는 호스트로 라우팅됨)
- Germany may be directed to the US (if that's the lowest latency)
[ Health Checks ]
설정한 Check Interval 의 수만큼 연속으로 instance (IP) 에 ping 을 날려 instance 의 상태를 파악
- Have 3 (default value is 3) health checks failed => unhealthy
- After 3 (default value is 3) health checks passed => health
- Default Health Check Interval : 30s (can set to 10s - higher cost)
- About 15 health checkers will check the endpoint health
=> one request every 2 seconds on average
- Can have HTTP, TCP and HTTPS health checks (no SSL verification)
- Possibility of integrating the health check with CloudWatch
* Health checks can be linked to Route53 DNS queries
[ Failover Routing Policy ]
1. Web browser 가 Route53 에 DNS 요청
2. Route 53 은 primary instance에 Health check
3. Primary instance 가 unhealthy 할 경우 secondary instance (DR(disaster recovery)) 에 요청
[ Geolocation Routing Policy ]
지역설정을 하여 해당 지역에서 오는 request 는 특정 A record 의 instance 가 처리
지정하지 않은 지역으로부터 요청이 올 경우 default 로 설정해놓은 A record 의 instance 가 처리
- Different from Latency based
- This is routing based on user location
- Here we specify : traffic from the UK should go to this specific IP
* Should create a "default" policy (in case there's no match on location)
[ Multi Value Routing Policy (=client side load balancing) ]
동일한 DNS 에 A record 를 최대 8개 까지 설정
client 에서 Route 53 에 DNS 요청시 healthy 한 instance 만 response
client 는 healthy 한 instance 중에서 하나의 instance에 random 하게 요청
- Use when routing traffic to multiple resources
- Want to associate a Route 53 health checks with records
- Up to 8 healthy records are returned for each Multi Value query
* Multi Value is not a substitute for having an ELB
[ # Hands-on : Route53 에 record, health check 설정 방법 ]
1. health check 생성 (instance IP or Domain 입력)
2. Route 53 의 record 생성
- Name : sample.testaws.com (sample 이 Record set 의 name 이자 domain 이 됨)
- Type : A record ( IPv4 )
- TTL : IP 유효시간 설정
- Value : Type의 value 로, A record 선택시 인스턴스의 IPv4 입력
- Routing Policy : simple(단일 A record), failover, geolocation, latency, weighted, multi value.. 선택
3. 선택한 record 의 Routing Policy 에 따라 Associate with Health check 옵션 Yes 로 선택 및 Health Check 선택
: 위와 같이 설정시 client 는 DNS 요청을 Route53 에 하며 health check 를 통해 주기적으로 ping 을 하여 IP의 instance 가 healthy/unhealty 한지 파악. 인스턴스의 상태에 따라 선택한 Routing Policy 에 따라 다르게 동작
[ Route 53 as a Registrar ]
Rregistrar 는 예약된 Internet domain names을 관리하는 조직
- A domain name registrar is a organization that manages the reservation of Internet domain names
(eg. Google Domains, and also Route53(AWS))
* Domain Registrar != DNS (but each domain registrar usually comes with some DNS features)
# 3rd Party Registrar with AWS Route 53
3rd Party 에서 AWS Route53 의 DNS 서버 사용하기
1) 3rd Party (ex: Google) 가 제공하는 Name Server 대신 Custom Name Server 를 사용하도록 설정
2) 이때 Custom Name Server 는 Route53 에서 생성한 Hosted Zone 의 Name Server 로 설정 (Hosted Zone 생성 후 Hosted Zone 클릭시 노출되는 Details 정보 안에 Name Server 정보가 있음)
- If you buy your domain on 3rd party website, you can still use Route53
1) Create a Hosted Zone in Route53
2) Update NS Records on 3rd party website to use Route53 name servers
'infra & cloud > AWS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [AWS] 7-1. Amazon S3, S3 Encryption (0) | 2021.03.29 |
|---|---|
| [AWS] 6. Beanstalk (0) | 2021.03.29 |
| [AWS] 4-3. ElastiCache, Redis, MemCached (0) | 2021.03.23 |
| [AWS] 4-2. Aurora (0) | 2021.03.23 |
| [AWS] 4-1. RDS, Read Replicas, DR (0) | 2021.03.22 |



