[ Databases in AWS : S3 ]
- S3 is a key / value store for objects
- Great for big objects, not so great for small objects
- Serverless, sclaes infinitely, max object size is 5 TB
- Strong consistency
- Tiers : S3 Standard, S3 IA, S3 One Zone IA, Glacier for backups
- Features : Versioning, Encryption, Cross Region Replication, etc...
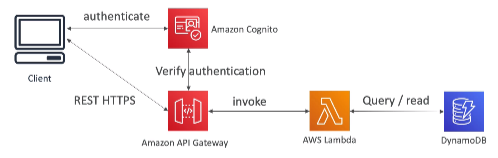
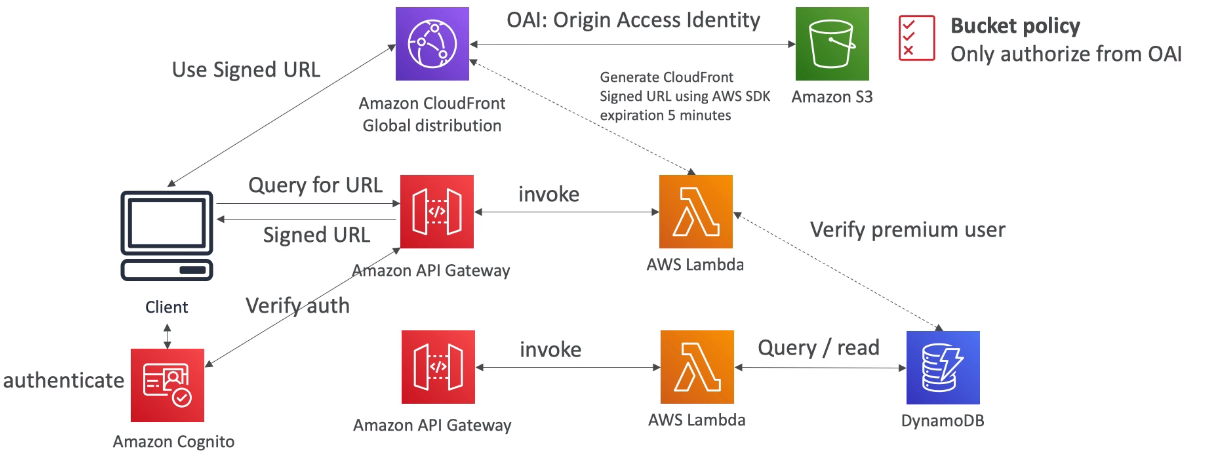
- Security : IAM, Bucket Policies, ACL(Access Control Policy)
- Encryption : SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, SSE-C, client side encryption, SSL in transit
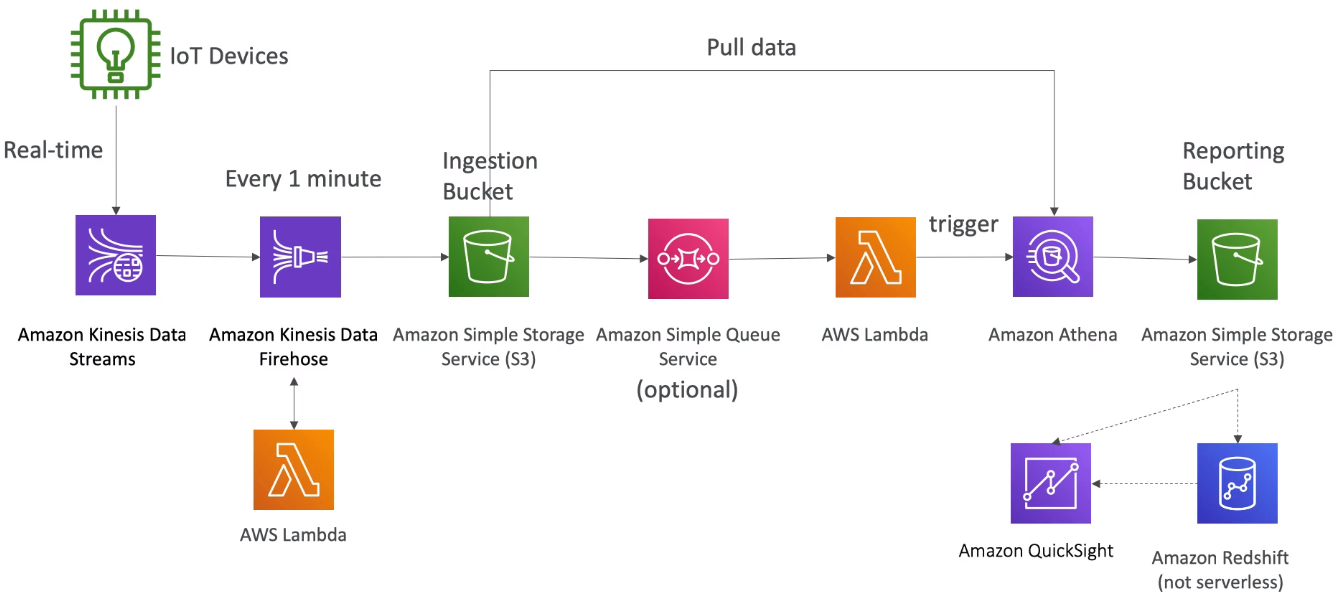
※ Use Case : static files, key value store for big files, website hosting
[ S3 for Solutions Architect ]
Operations : no operations needed
Security : IAM , Bucket Policies, ACL, Encryption (Server/Client), SSL
Reliability : 99.99% durability / 99.9% availability, Multi AZ, CRR(Cross Region Replication)
Performance : scales to thousands of read/writes per second, transfer acceleration/multi-part for big files
Cost : pay per storage usage, network cost, requests number
'infra & cloud > AWS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [AWS] 18-7. Databases in AWS : Redshift (0) | 2021.09.25 |
|---|---|
| [AWS] 18-6. Databases in AWS : Athena (0) | 2021.09.25 |
| [AWS] 18-5. Databases in AWS : DynamoDB (0) | 2021.09.25 |
| [AWS] 18-4. Databases in AWS : ElastiCache (0) | 2021.09.23 |
| [AWS] 18-3. Databases in AWS : Aurora (0) | 2021.09.23 |